21 Best Sources of the Good Cholesterol
Higher levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL), commonly known as the “good” cholesterol, is generally associated with a lower risk for heart disease. Several lifestyle choices we make, including a change in diet, can significantly reduce the risk of developing diseases that are related to high cholesterol.hsg
What is HDL Cholesterol?
HDL is a protective form of cholesterol that carries the bad cholesterol away from your blood vessels (the arteries) into your liver. There it is broken down, then eliminated from the body. When your HDL is 60mg/dl or higher, you are considered to have reduced risk for heart attack or heart diseases. On the other hand, when your HDL is low (below 40mg/dl for men or less than 50mg/dl for women), your chances of having a heart attack is increased.
Below are heart-healthy foods that naturally elevate HDLs. You should consider consuming these more often to protect you from heart disease or stroke, among other preventable medical conditions.
Antioxidant-rich food– diets rich in antioxidants elevate HDL cholesterol in relation to triglycerides. Common examples of high antioxidant foods include berries, beets, dark chocolate, purple cabbage, red grapes, spinach, kale, red bell peppers, and most deeply colored vegetables and fruits.
Vitamin E, an antioxidant supplement containing mixed forms of tocopherols, leads the list for supplements that have been proven to manage cholesterol optimally.
Avocado– according to the Journal of the American Heart Association, this fatty, creamy fruit is an excellent source of monounsaturated fats shown to be potent HDL boosters. Apart from this, you’ll be happy to know that it also lowers the bad cholesterol accumulating in the body.
This can be a perfect choice as a sandwich topping or an ingredient for your favorite salad.
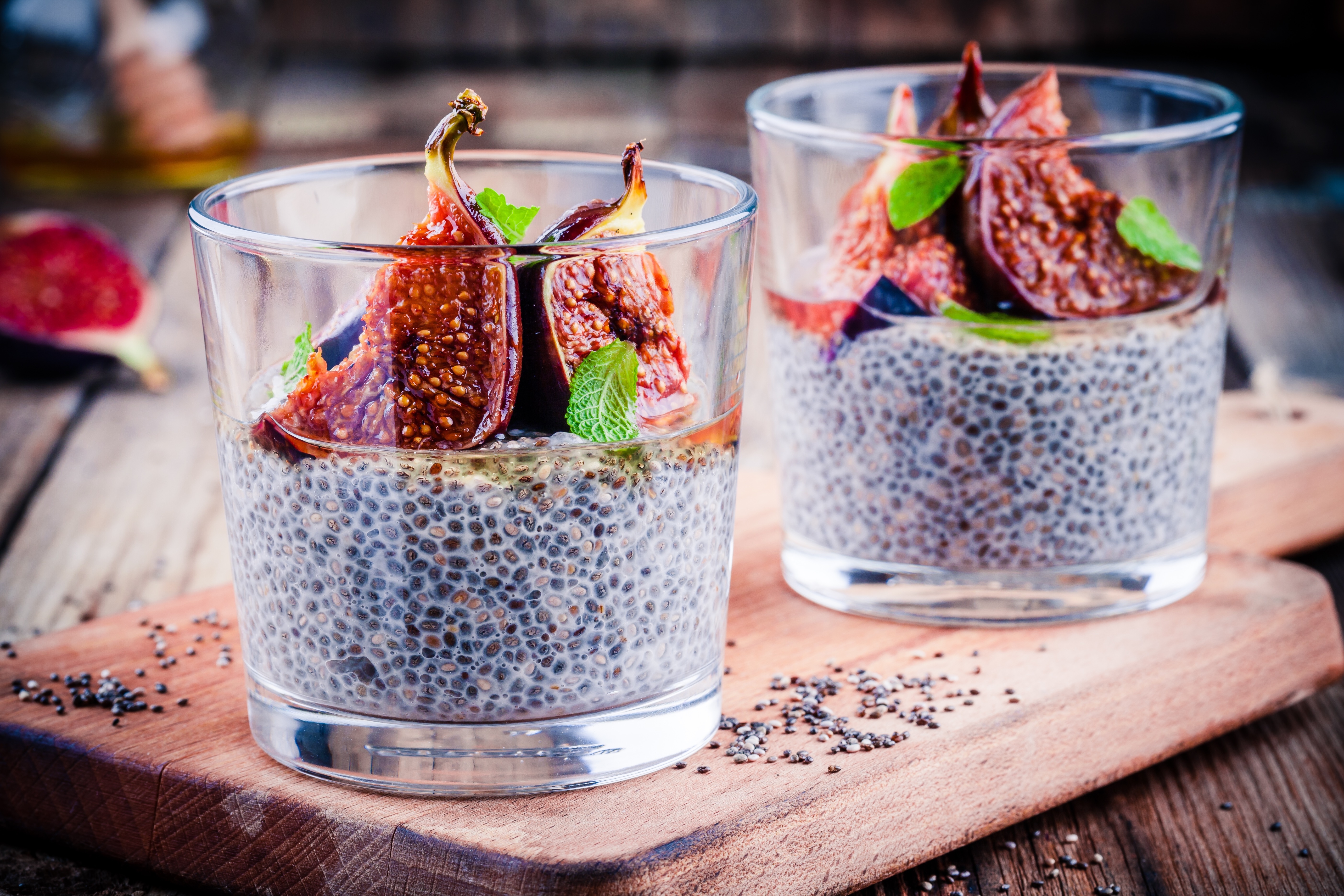
Chia seeds– this is a good source of plant-based omega 3 fats, fiber, and other essential nutrients. Apart from raising good cholesterol and reducing bad cholesterol, adding chia seeds to your diet may help normalize your blood pressure.
It’s a great idea to sprinkle Chia seeds on your favorite oatmeal cereal, salads, yogurt, dips, or smoothies. Also, you can add them to your baked goods instead of eggs.
Red wine- contains polyphenols that can be a protective agent for your heart. Research shows that the moderate consumption of this type of wine can help in preventing heart-related diseases due to its potent antioxidant effects. Particularly, it increases good cholesterol and reduces the negative effects of platelets in the blood.
Be sure to enjoy the drink in moderation.
As an alternative, you can drink de-alcoholized versions of red wine, as this should offer similar health benefits.
Almonds– eating this type of nuts regularly, according to several US studies, can boost your HDL, as well as your overall functionality. This makes almonds a smart choice for a heart-healthy snack. Apart from this, regular consumption can also provide you with good doses of vitamin E and fiber.
This is not a cure-all solution to cholesterol issues, but when eaten in moderation, can enhance your health optimally.
Calcium Rich Foods– this mineral does not only strengthen your bones but also your heart. Evidence reveals that people who live in locations where calcium is present in hard water have lower incidences of deaths due to heart-related conditions. Also, calcium, apart from binding to cholesterol to prevent the latter’s absorption, increases HDL cholesterol.
Approximately 1000 mg of calcium raises good cholesterol by 1-5% while lowering bad cholesterol by 2-6%.
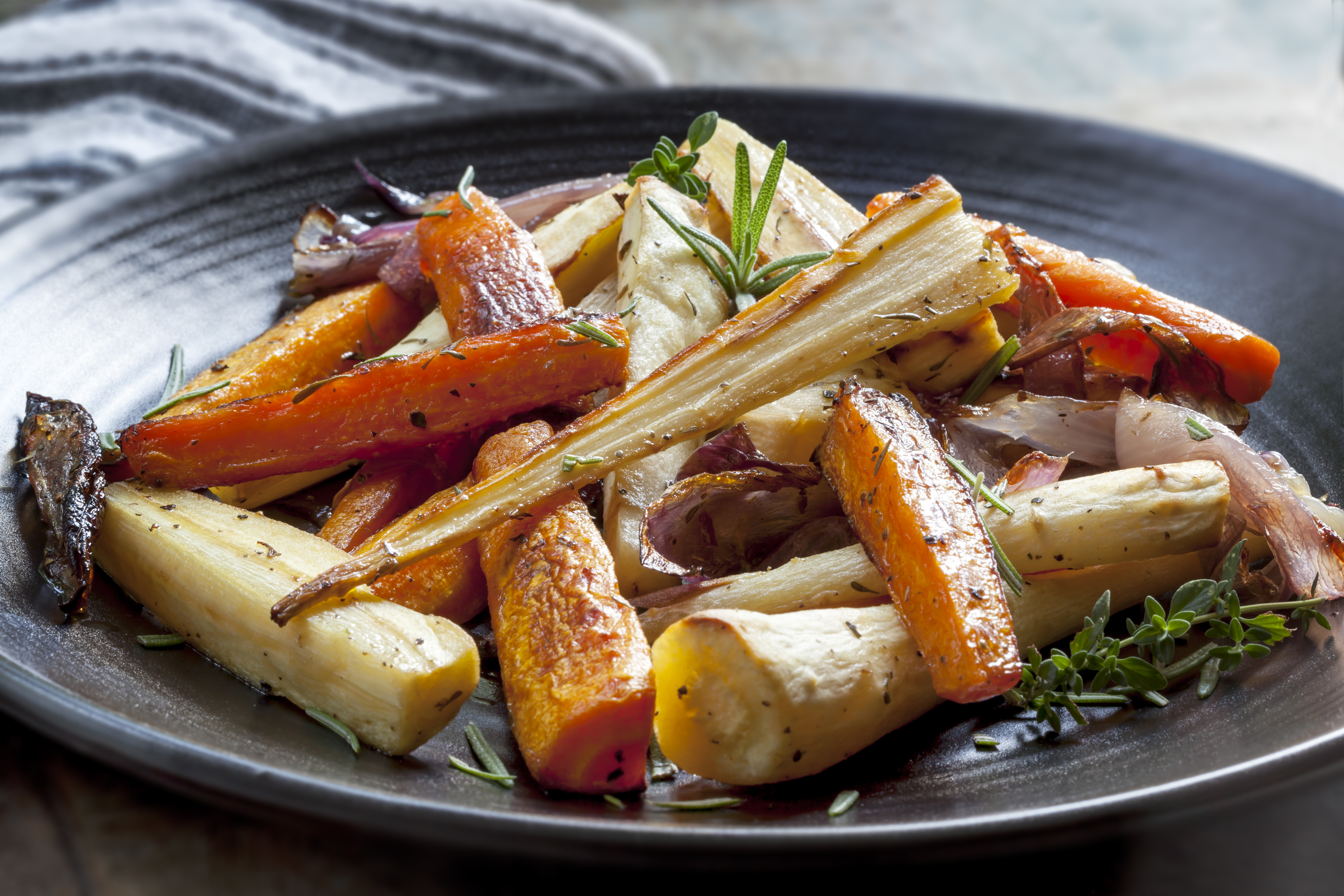
Carrots– you can count on carrots to raise your levels of HDL. Carrots are full of anti-cholesterol soluble fiber, such as pectin, that regulates your cholesterol levels. Several studies have revealed that the amounts of beta carotene in one or two carrots can boost your good HDLs significantly.
Whether you would have your carrots cooked, raw, canned, frozen, chopped, or even liquefied, the fiber content remains therapeutic.
Chocolates– an interesting study from Harvard University reveals that individuals who ate chocolates several times a month lived longer and were healthier than those who abstained. Another British Medical Journal study observed the same phenomenon in a study on longevity and traced it directly to chocolates. Moreover, an increase in good cholesterol and a favorable action against the formation of blood clots which can lead to stroke/heart attack has been observed.
Antioxidants in chocolate are highest and promote optimal heart health when they come from cocoa powder.
Apart from chocolate from cocoa powder, the next most effective form is dark chocolate which is rich in oleic acid– the kind of good fat in olive oil.
Third in line will be milk chocolate which is still very potent in antioxidants.
Fatty fish– several studies have shown an increase in HDL levels among heart disease patients who consumed fatty fish at least four times weekly. The omega 3 fats in fish provide tremendous benefits for heart health and better functioning of the cells that line your blood vessels (the arteries).
Examples of heart-healthy fatty fish to include in your regular diet are salmon, herring, mackerel, sardines, and anchovies.
Garlic– evidence has shown that garlic has an amazing impact in reducing the risk of heart-related conditions. Particularly, studies show that individuals who include garlic as a regular component of their diet, have raised levels of good cholesterol, as well as lowered bad cholesterol and triglycerides.
Regular consumers of garlic also enjoy normal or more regulated blood pressure and decreased stickiness of blood. Sticky blood can be a risk factor for heart attack or stroke due to the high tendency for clumping of blood.
Unsaturated fats– generally, you should choose this type of fats in your diet, instead of saturated ones. Unsaturated fats include monounsaturated fats (e.g., margarine spreads and oils, including canola, olive and peanut; some nuts, and avocados) and polyunsaturated fats (e.g., margarine spreads and oils, including soybean, safflower, and sunflower, oily fish, some seeds and nuts). They have been shown to raise HDLs and lower bad cholesterol.
The heart-protective effect from eating these foods rich in unsaturated fats is believed to partially explain why people who take Mediterranean diets (e.g., diets rich in olive oil) live healthy and longer lives.
These types of fats are also present in rapeseed oil, cashews, walnuts, almonds, and most other types of nuts. Just by having a single serving of nuts five times weekly, you can significantly reduce your risk for heart disease!
Unsaturated fats are also found in plant-based products such as most vegetable oils, seeds, and whole grains. A non-plant source of these good fats is fatty or deepwater fish. It is particularly a rich source of polyunsaturated fats.
Alcohol– moderate alcohol consumption has shown beneficial effects to major organs of the body such as the heart and brain according to studies from Johns Hopkins University in Maryland. Alcohol has the potential to relax one’s mood, muscles, lower blood pressure temporarily, and expand blood vessels. This can lead to reduced risk for heart diseases. Drinking moderate amounts of alcohol has shown to increase HDLs in the blood.
Although red wine has gotten more attention with regards to the beneficial effects of alcohol, controlled studies show similar positive effects with all forms of alcoholic beverages, including wine, beer, and spirits.
Herbs & Supplements– Some popular herbs and supplements boost the good cholesterol in the body.
A supplement called Policosanol has shown to raise HDLs while lowering LDLs. This substance is derived from the surface of a sugarcane plant. It is available as a supplement in pill form.
Guggul or Gugulipid has been used as an ancient herb in Indian cultures for centuries. It has proven to raise HDL and reduce both triglycerides and LDLs. Its antioxidant properties act against blood clumping that may lead to a heart attack or stroke. Guggul pill supplements are made from the Mukul myrrh tree.
Niacin (also known as Vitamin B3), in several researches, has significantly raised HDLs, while also slightly reducing triglycerides levels. To be most effective, it has been recommended to take Niacin according to doses advised by your physician, typically three times a day with meals.
Ketogenic diets– this diet regimen, when consumed regularly, has shown to increase HDL cholesterol. This is true especially in individuals who have a tendency to have lower levels of good cholesterol. Moreover, this high fat and very low-carbohydrate diet can provide you with a range of health benefits, including reduced blood sugar and weight loss.
The diet limits carbohydrates to 20 to 50 grams per day only.
Some healthy options to eat for a ketogenic diet include low-carbohydrate vegetables, seafood, avocados, cheese, meat (especially the grass-fed types) and poultry, eggs, plain yogurt, olive oil, nuts, seeds, berries, butter and cream, olives, unsweetened coffee and tea, dark chocolate and cocoa powder.
Coconut oil– evidence shows that coconut oil may increase your metabolism and protect major organs of the body while reducing appetite. It was once an issue that coconut oil may not be good for the heart because of its high content of saturated fat. It appears, however, that this oil is actually heart-healthy. It has been proven to raise HDL cholesterol more than most types of fats.
Consuming two tablespoons or 30 ml of coconut oil daily may help increase your good cholesterol levels.
Purple fruits and vegetables– Purple-colored fruits and vegetables can be a delicious way of potentially increasing HDLs. Purple produce is thought to contain anthocyanins, a potent type of antioxidant. Several studies of anthocyanin extracts have shown to raise the good cholesterol, as well as fight inflammation, protect cells from the damage of free radicals, and contain anti-cancer and anti-viral properties.
Consuming vegetables and fruits rich in anthocyanins (e.g., cherries, cranberries, blueberries, blackberries, eggplant, plums, prunes, and grape juice) provide a protective effect to heart health.
Whole grains– oatmeal, cereals, bran, wild or brown rice, and whole-grain bread gives your HDL cholesterol a percentage boost, by lowering your total cholesterol, and LDLs. This is primarily attributed to its soluble fiber content that’s known to optimize your cholesterol levels.
It’s recommended to have at least two helpings of whole grains daily.
Legumes– beans and legumes, like whole grains, are a great source of soluble fiber. Having these as yummy side dishes can boost your good cholesterol and keep your values at optimal levels. Nutritious examples include black-eyed peas, kidney and black beans, lentils, and navy beans.
These beans also contain folate, an important B vitamin, that keeps your heart healthy. Canned beans will contain only half as much folate as cooked dry beans.
High fiber fruits– apples, pears, and prunes can both raise your HDL cholesterol and lower your LDL cholesterol. You can cut them up and stir them into an oatmeal or cereal dish, or blend them to make a delicious smoothie. They contain the same healthy and tasty benefits when taken solo as your afternoon snack or after-dinner treat.
Flax– many vegetarians take flax seeds because these are clearly from plant-based sources, and contain the heart-healthy types of fats. Particularly, flaxseed oil and ground flax seeds contain omega 3 fats.
It’s a great idea to sprinkle flax seeds on your morning oatmeal, cereals, salads, yogurt, or dips. You can alternatively add them to your baked goods. Flaxseed oil can also be a welcome addition to smoothies or salad dressings.
Soy– this isn’t just for vegetarians. Having soy in your diet is a great alternative to reduce meat consumption. Eating less meat regularly naturally leads to elevated HDLs and decreased LDLs.
Some critics insist that the benefits in cholesterol levels are a result of eating less meat rather than because of consuming soy particularly.
For a tasty soy appetizer, you can steam unsalted edamame or use it as a healthy type of spread during parties. Tofu is another popular type of soy product, many vegetarians love.
Cholesterol can be significantly influenced by your diet, as well as physical activity, smoking, stress, and body weight. By making changes in these areas, you can lessen your chances of disability or early death. For your diet, making wise changes such as choosing fewer calories and bad fats can make a big difference. Your body needs to take in more nutrients, fiber, and good fats to balance or optimize your cholesterol levels.
The changes you choose to do to keep your cholesterol within normal can also reduce your risk for heart-related diseases. Eating healthy foods regularly and keeping a healthy lifestyle should show in your optimized blood pressure, blood sugar, and weight. Overall, by understanding cholesterol and the types of food that could improve your good cholesterol values, you will be able to make tremendous changes for your health.